🚨 BOLO 👉 CRITICAL SECURITY ALERT: 224 Malicious Android Apps Bypass Google Play Store Defenses – Essential Protection Guide for Legal Professionals!
/224 Malicious Android Apps Detected – Lawyers Must Act Now to Protect Client Data!
Recent cybersecurity intelligence reveals that 224 malicious Android applications successfully circumvented Google Play Store's anti-malware systems through a sophisticated campaign dubbed "SlopAds". This represents a significant escalation in mobile security threats that demands immediate attention from legal professionals who increasingly rely on mobile devices for client communications and case management.
The Threat Mechanism 🎯
The SlopAds campaign employs a cunning two-stage attack strategy. When users download these applications directly from Google Play Store searches, they function as advertised. However, apps downloaded via targeted advertising campaigns secretly install encrypted configuration files that subsequently deploy malware onto devices. This technique successfully evaded Google's standard security reviews by appearing benign during initial screening.
The malicious applications typically masqueraded as simple utilities or attempted to impersonate popular applications like ChatGPT. Once activated, the malware harvests device information and generates fraudulent advertising impressions, potentially compromising sensitive data and device integrity.
Why Legal Professionals Face Elevated Risk ⚖️
Legal practitioners encounter disproportionate cybersecurity risks due to several converging factors. Law firms handle exceptionally sensitive data including privileged attorney-client communications, merger and acquisition details, intellectual property, medical records, and confidential case strategies. This makes legal professionals prime targets for sophisticated threat actors seeking valuable information.
Recent data indicates that over 110 law firms reported data breaches in 2022 alone, exceeding previous years and demonstrating an escalating trend. The consequences of mobile device compromise extend beyond data theft to include potential malpractice liability, ABA ethics violations under Model Rules 1.1 (Competence), 1.1(8) (Tech Competence) and 1.6 (Confidentiality), state bar disciplinary action, regulatory compliance fines, and permanent reputational damage.
Mobile devices present particularly acute risks because they often contain both personal and professional data, blur the boundaries between work and personal use, and are easily misplaced or stolen. Interestingly, twenty-five percent of data breaches in financial services since 2006 resulted from lost or stolen devices, highlighting the vulnerability of mobile platforms.
Comprehensive Protection Strategy 🛡️
Immediate Device Security Measures
Law Firm Cybersecurity Framework: Policies, Training, and Incident Response for Mobile Threats.
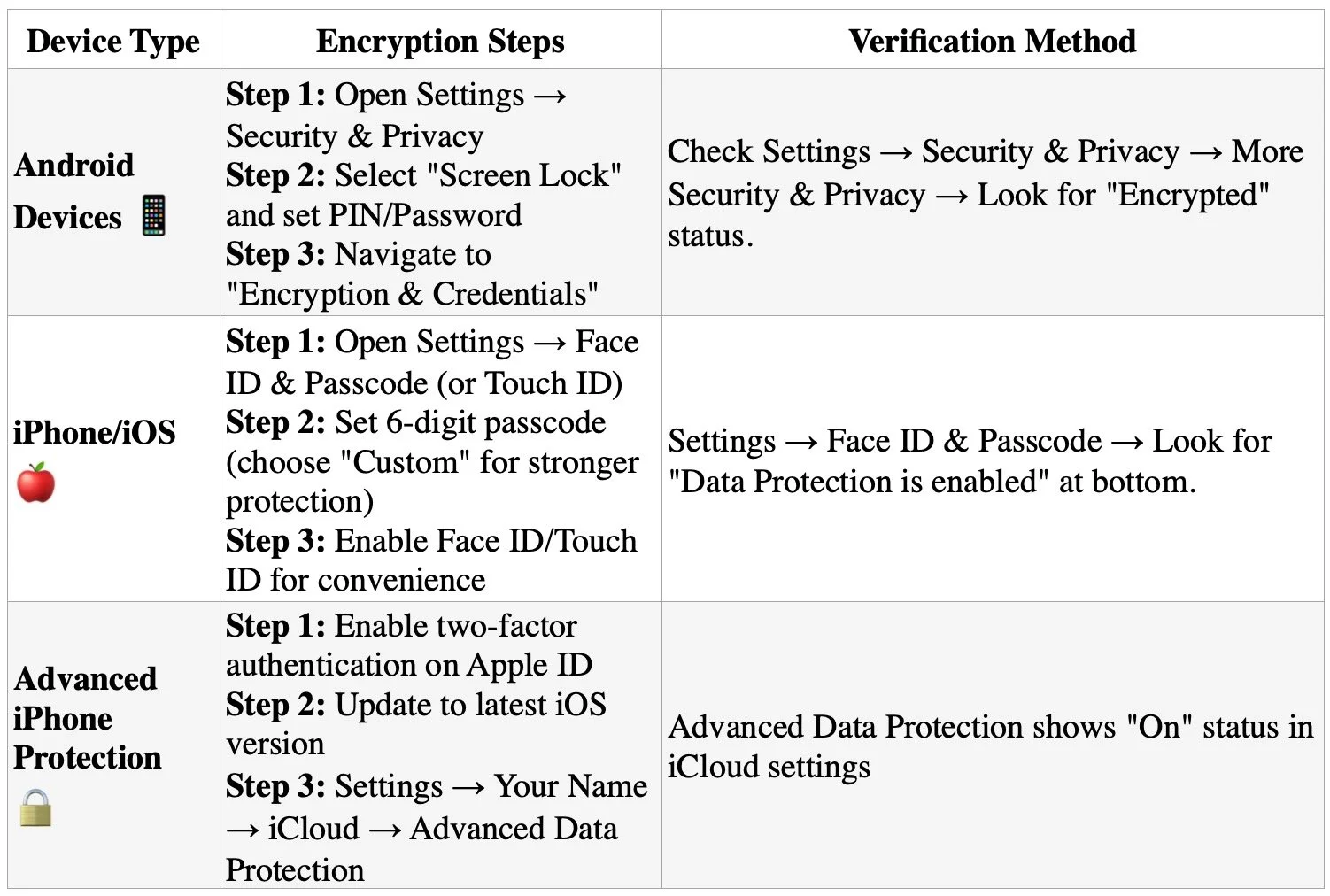
Enable full-device encryption on all smartphones and tablets used for any professional purposes. This critical step ensures that even if devices are physically compromised, sensitive data remains protected. Modern Android devices (version 6.0+) and iPhones automatically enable encryption when a screen lock is configured, but verification and proper setup remain essential.
Critical Implementation Notes
Android devices must remain plugged into power during the encryption process, which takes approximately one hour and cannot be interrupted;
Choose complex passcodes rather than simple PINs or patterns - six-digit minimum for iPhones, with alphanumeric options preferred;
Most devices since Android 6.0 and iOS 8 enable encryption by default when screen locks are configured, but manual verification is essential;
For maximum security on iPhones, enable the "Erase Data" feature after 10 failed attempts for devices containing highly sensitive information.
Implement strong, unique passwords or biometric authentication rather than simple PINs or patterns. The encryption key derives directly from your lock screen credentials, making password strength critical for data protection. For legal professionals handling privileged communications, this represents the first line of defense against unauthorized access to confidential client information.
some stepts to Enable full-device encryption on all smartphones and tablets used for any professional purposes.
Application Security Protocols
Download applications exclusively from official app stores and carefully review all requested permissions before installation. Be particularly vigilant about apps requesting "Display over other apps" permissions, as these can enable malware to hijack device functionality. Remove any unused applications regularly and avoid third-party app stores entirely.
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Implementation
Deploy comprehensive MDM solutions that enforce security policies across all firm devices. MDM systems should include capabilities for remote data wiping, automatic security updates, app blacklisting, and real-time threat detection. These systems provide centralized control over device security while maintaining user productivity.
Authentication and Access Controls
Mandate multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all professional applications and accounts. Use authentication apps or hardware tokens rather than SMS-based codes, which can be intercepted. Implement biometric authentication where available for an additional security layer.
Network Security Measures
Utilize Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) when accessing firm resources from public Wi-Fi networks. Ensure all communications involving client data occur through encrypted channels such as secure client portals rather than standard email or messaging applications.
Advanced Protection Considerations 🔍
Regular Security Assessments
BE Your firm’s heao! Know the Essential Mobile Security Protocols Every Lawyer Needs: Encryption, MFA, and VPN Protection!
Perform periodic security audits of all mobile devices and applications used within the firm. These assessments should identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance with security policies, and evaluate the effectiveness of existing protections.
Secure Communication Channels
Implement client portals and secure messaging platforms specifically designed for legal communications. These systems provide encrypted data transmission and storage while maintaining audit trails for compliance purposes.
Data Backup and Recovery
Maintain regular, encrypted backups of all mobile device data with tested recovery procedures. This ensures business continuity in case of device compromise or loss while protecting sensitive information.
The SlopAds malware campaign demonstrates that traditional security assumptions about official app stores no longer provide adequate protection. Legal professionals must adopt a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to mobile security that addresses both technical vulnerabilities and human factors. By implementing these protective measures proactively, law firms can significantly reduce their exposure to mobile-based cyber threats while maintaining the productivity benefits of mobile technology.
Stay Safe Out There!