"How To": Lawyers Choosing the Right “AI Browsers” While Protecting Client Data: Complete Guide 2025 🔒⚖️
/The question is whether lawyers should be using “AI Browsers” right now?
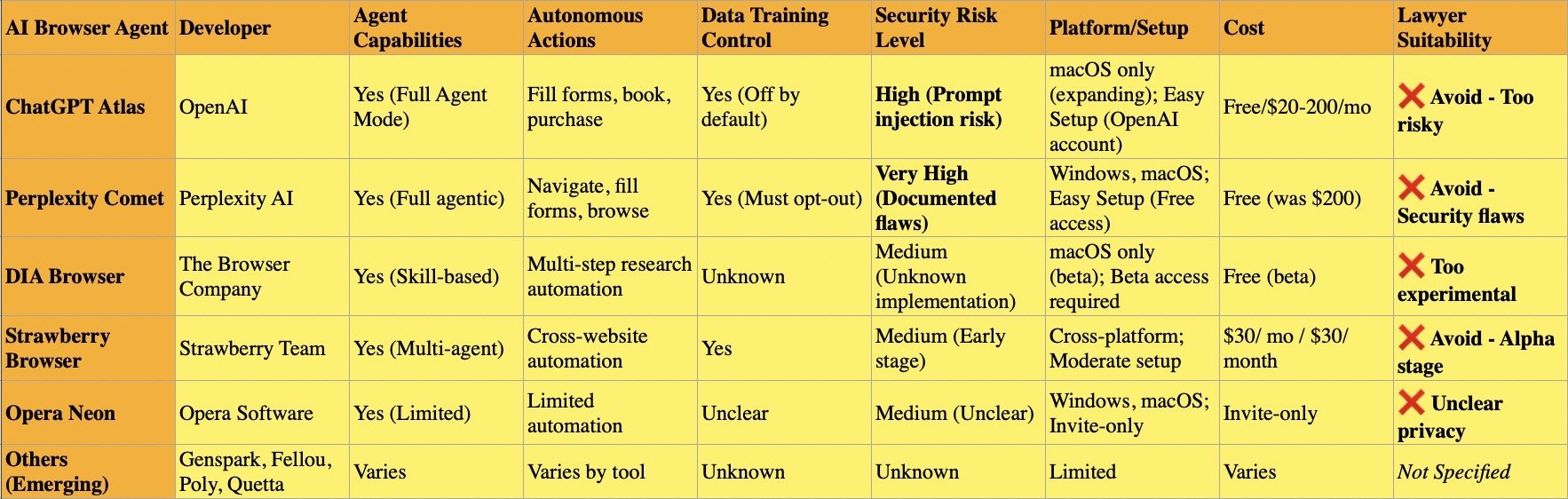
AI browsers represent a fundamental shift from traditional web browsing. Unlike Chrome or Firefox with AI features bolted on, dedicated AI browsers like ChatGPT Atlas, Perplexity Comet, DIA Browser, and Strawberry Browser were built from the ground up around artificial intelligence. These tools don't just help you browse—they browse for you, making autonomous decisions, filling forms, booking reservations, and completing multi-step tasks through "agentic" capabilities that require extensive access to your data.
For lawyers, this autonomy creates unacceptable confidentiality risks. Security researchers discovered that AI browsers suffer from critical "prompt injection" vulnerabilities where malicious code hidden on websites tricks the AI into stealing emails, accessing calendars, and exfiltrating confidential files. When you ask an AI browser to "summarize this page," it processes both visible content and invisible malicious instructions without distinguishing between them.
The AI Training Threat
Most AI browsers automatically train on your browsing data unless you manually opt out. This means privileged attorney-client communications, case research, and client information could become embedded in AI training datasets permanently. Once data trains an AI model, removing it becomes impossible—it persists indefinitely in the neural network's learned patterns.
ChatGPT Atlas defaults to excluding browsing content from training, but users must verify this setting remains disabled in Data Controls. Perplexity Comet automatically opts users into AI training on browsing data and search queries unless you manually disable the Data Retention toggle in Account Settings. Strawberry Browser and DIA Browser have unclear or unknown training policies, making them inappropriate for client work. Samsung banned ChatGPT after employees accidentally exposed proprietary code this way.
The Leading Dedicated AI Browsers
Perplexity Comet positions itself as a research-focused "answer engine" with citation-first design. However, security researchers at Brave documented severe vulnerabilities including screenshot attacks where nearly invisible text tricks the AI into executing unauthorized commands. Comet's autonomous agent can navigate websites, fill shopping carts, and cancel subscriptions independently—impressive for productivity but catastrophic for confidentiality when exploited.
ChatGPT Atlas integrates OpenAI's models into a Chromium-based browser with Agent Mode for automating tasks. Currently macOS-only with other platforms coming soon, Atlas provides contextual memory across browsing sessions and can access connected services like email and calendars. While OpenAI implements some safeguards, security experts emphasize no AI agent browser has adequate protections for confidential information.
Strawberry Browser, developed by a Swedish team, focuses on multi-agent automation with "AI Companions" that learn your patterns and work across multiple websites simultaneously. Still in alpha/beta stage at $30/month, Strawberry demonstrates extensive autonomous capabilities but remains too experimental for legal practice.
DIA Browser from The Browser Company redesigns browsing around AI-powered tab organization and workflow memory. In limited beta, DIA uses AI to remember research habits and enable conversational interaction with open tabs. The experimental nature and unclear privacy policies make it inappropriate for client work.
Opera Neon and emerging alternatives (Genspark, Fellou, Poly, Quetta) remain in early stages with insufficient track records or unclear privacy practices for legal professional evaluation.
Critical Recommendations for Lawyers
Avoid all AI agent browsers for client-related work. PCMag's extensive testing concluded: "Given their dubious value, poor performance, and privacy concerns, I don't think AI web browsers are worth using" over traditional alternatives.
If you experiment with AI browsers personally, do so only for non-confidential tasks. Disable all training features immediately. Use separate devices that never access client files, emails, or practice management systems. Understand that prompt injection attacks remain threats regardless of privacy settings.
Traditional browsers (Firefox, Brave, Safari) with proper privacy configurations remain your only safe option. Your Rule 1.6 obligations require recognizing when new technology poses unacceptable confidentiality risks.
Lawyers should know what risks come with using AI Browsers!