🧪🎧 TSL Labs Bonus Podcast: Open vs. Closed AI — The Hidden Liability Trap in Your Firm ⚖️🤖
/Welcome to TSL Labs Podcast Experiment. 🧪🎧 In this special "Deep Dive" bonus episode, we strip away the hype surrounding Generative AI to expose a critical operational risk hiding in plain sight: the dangerous confusion between "Open" and "Closed" AI systems.
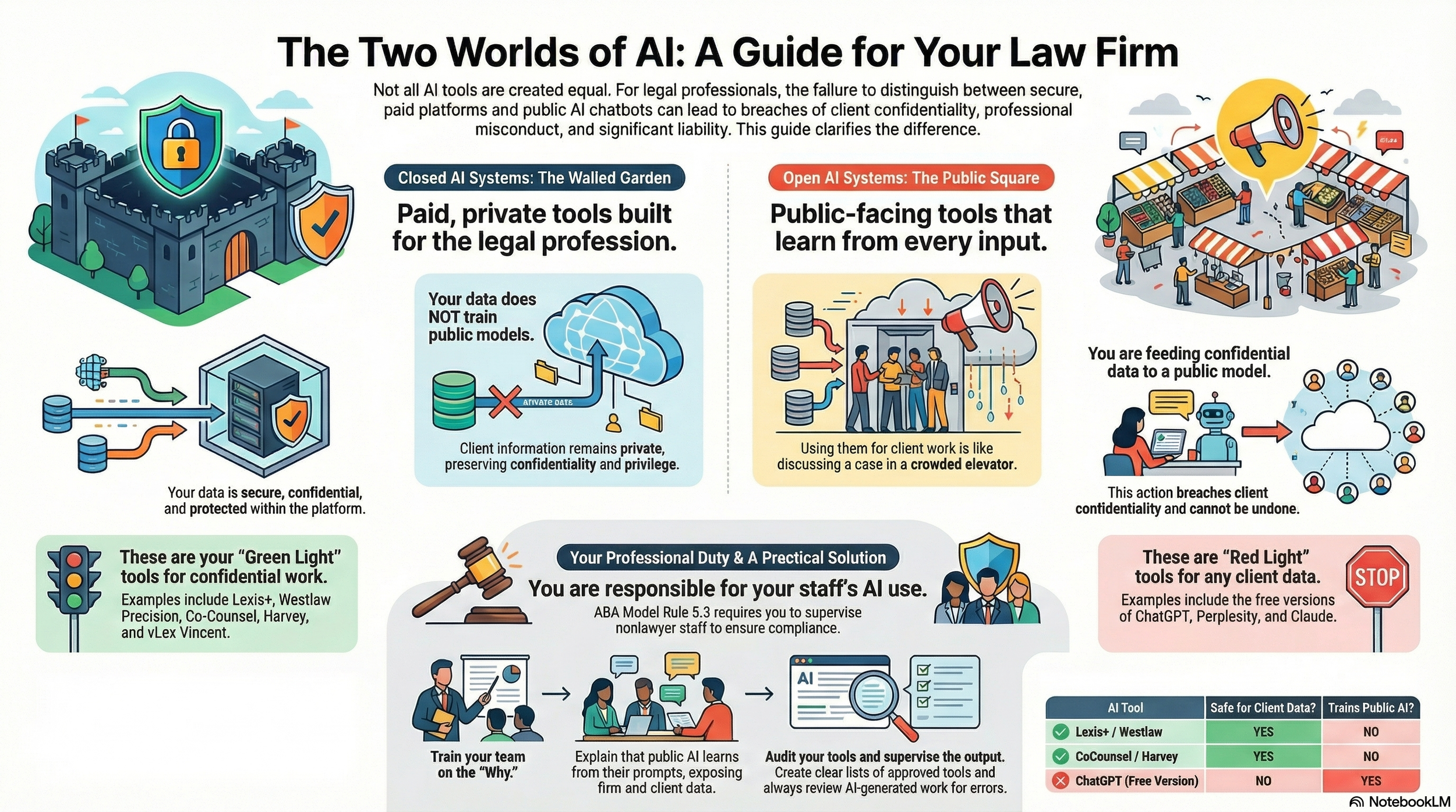
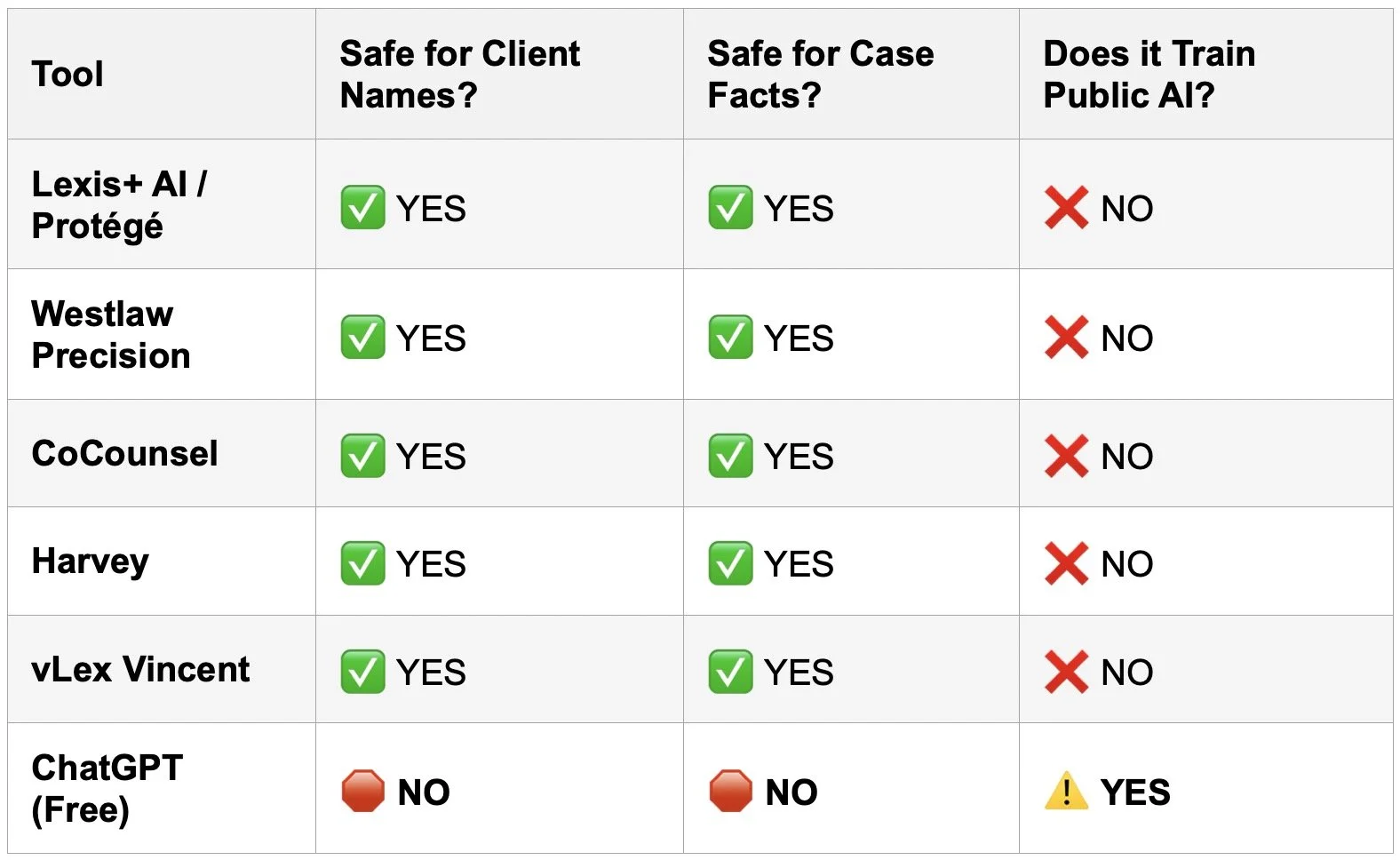
Featuring an engaging discussion between our Google Notebook AI hosts, this episode unpacks the "Swiss Army Knife vs. Scalpel" analogy that every managing partner needs to understand. We explore why the "Green Light" tools you pay for are fundamentally different from the "Red Light" public models your staff might be using—and why treating them the same could trigger an immediate breach of ABA Model Rule 5.3. From the "hidden crisis" of AI embedded in Microsoft 365 to the non-negotiable duty to supervise, this is the essential briefing for protecting client confidentiality in the age of algorithms.
In our conversation, we cover the following:
[00:00] – Introduction: The hidden danger of AI in law firms.
[01:00] – The "AI Gap": Why staff confuse efficiency with confidentiality.
[02:00] – The Green Light Zone: Defining secure, "Closed" AI systems (The Scalpel).
[03:45] – The Red Light Zone: Understanding "Open" Public LLMs (The Swiss Army Knife).
[04:45] – "Feeding the Beast": How public queries actively train the model for everyone else.
[05:45] – The Duty to Supervise: ABA Model Rules 5.3 and 1.1[8] implications.
[07:00] – The Hidden Crisis: AI embedded in ubiquitous tools (Microsoft 365, Adobe, Zoom).
[09:00] – The Training Gap: Why digital natives assume all prompt boxes are safe.
[10:00] – Actionable Solutions: Auditing tools and the "Elevator vs. Private Room" analogy.
[12:00] – Hallucinations: Vendor liability vs. Professional negligence.
[14:00] – Conclusion: The final provocative thought on accidental breaches.
RESOURCES
Mentioned in the episode
ABA Model Rule 5.3 (Responsibilities Regarding Nonlawyer Assistance): https://www.americanbar.org/groups/professional_responsibility/publications/model_rules_of_professional_conduct/rule_5_3_responsibilities_regarding_nonlawyer_assistant/
ABA Model Rule 1.1, Comment 8 (Technology Competence): https://www.americanbar.org/groups/professional_responsibility/publications/model_rules_of_professional_conduct/rule_1_1_competence/ and https://www.americanbar.org/groups/professional_responsibility/publications/model_rules_of_professional_conduct/rule_1_1_competence/comment_on_rule_1_1/#:~:text=of%20these%20Rules.-,Maintaining%20Competence,all%20continuing%20legal%20education%20requirements%20to%20which%20the%20lawyer%20is%20subject.,-Back%20to%20Rule
Software & Cloud Services mentioned in the conversation
Lexis+ AI (LexisNexis): https://www.lexisnexis.com/en-us/products/lexis-plus-ai.page
Protégé (LegalMation/LexisNexis context): https://www.lexisnexis.com/en-us/products/lexis-plus-ai.page
Westlaw Precision (Thomson Reuters): https://legal.thomsonreuters.com/en/products/westlaw-precision
Co-Counsel (Casetext/Thomson Reuters): https://casetext.com/co-counsel
Harvey AI: https://www.harvey.ai/
vLex Vincent AI: https://vlex.com/vincent-ai
ChatGPT (OpenAI): https://chat.openai.com/
Perplexity AI: https://www.perplexity.ai/
Claude (Anthropic): https://claude.ai/
Microsoft 365 Copilot (Teams/Word): https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/enterprise/copilot
Adobe Creative Cloud (AI features): https://www.adobe.com/ai/overview.html
Zoom AI Companion: https://www.zoom.us/aihttps://www.zoom.com/en/products/ai-assistant/