MTC: AI may not be your co‑counsel—and a recent SDNY decision just made that painfully clear. ⚖️🤖
/SDNY Heppner Ruling: Public AI Use Breaks Attorney-Client PrivilegE!
In United States v. Heppner, Judge Jed Rakoff of the Southern District of New York ruled that documents a criminal defendant generated with a publicly accessible AI tool and later sent to his lawyers were not protected by either attorney‑client privilege or the work‑product doctrine. That decision should be a wake‑up call for every lawyer who has ever dropped client facts into a public chatbot.
The court’s analysis followed traditional privilege principles rather than futuristic AI theory. Privilege requires confidential communication between a client and a lawyer made for the purpose of obtaining legal advice. In Heppner, the AI tool was “obviously not an attorney,” and there was no “trusting human relationship” with a licensed professional who owed duties of loyalty and confidentiality. Moreover, the platform’s privacy policy disclosed that user inputs and outputs could be collected and shared with third parties, undermining any reasonable expectation of confidentiality. In short, the defendant’s AI‑generated drafts looked less like protected client notes and more like research entrusted to a third‑party service.
For sometime now, I’ve warned on The Tech‑Savvy Lawyer.Page has warned practitioners not to paste client PII or case‑specific facts into generative AI tools, particularly public models whose terms of use and training practices erode confidentiality. We have consistently framed AI as an extension of a lawyer’s existing ethical duties, not a shortcut around them. I have encouraged readers to treat these systems like any other non‑lawyer vendor that must be vetted, contractually constrained, and configured before use. That perspective aligns squarely with Heppner’s outcome: once you treat a public AI as a casual brainstorming partner, you risk treating your client’s confidences as discoverable data.
A Tech-Savvy Lawyer Avoids AI Privilege Waiver With Confidentiality Safeguards!
For lawyers, this has immediate implications under the ABA Model Rules. Model Rule 1.1 on competence now explicitly includes understanding the “benefits and risks associated” with relevant technology, and recent ABA guidance on generative AI emphasizes that uncritical reliance on these tools can breach the duty of competence. A lawyer who casually uses public AI tools with client facts—without reading the terms of use, configuring privacy, or warning the client—may fail the competence test in both technology and privilege preservation. The Tech‑Savvy Lawyer.Page repeatedly underscores this point, translating dense ethics opinions into practical checklists and workflows so that even lawyers with only moderate tech literacy can implement safer practices.
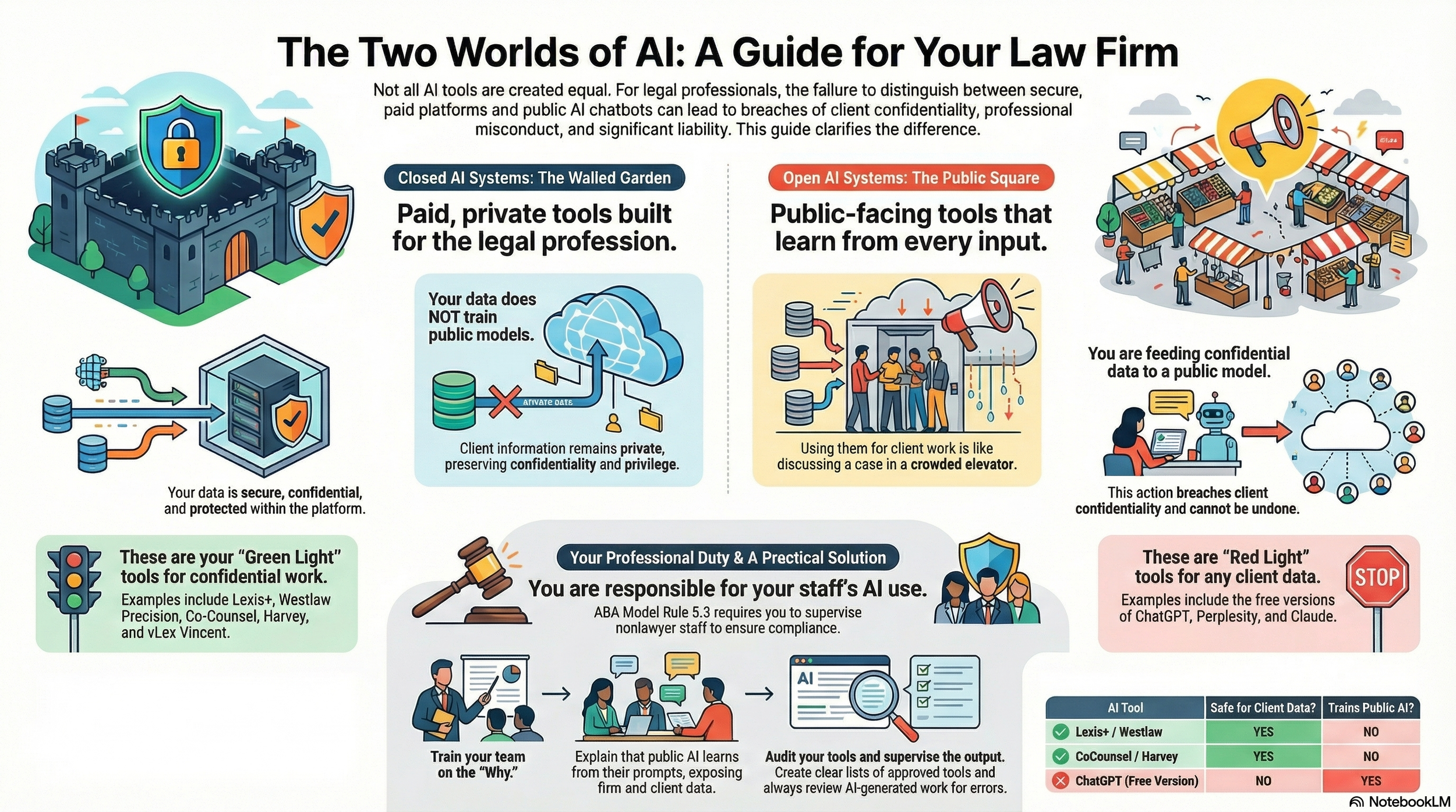
Model Rule 1.6 on confidentiality is equally implicated. If a lawyer discloses client confidential information to a public AI platform that uses data for training or reserves broad rights to disclose to third parties, that disclosure can be treated like sharing with any non‑necessary third party, risking waiver of privilege. Ethical guidance stresses that lawyers must understand whether an AI provider logs, trains on, or shares client data and must adopt reasonable safeguards before using such tools. That means reading privacy policies, toggling enterprise settings, and, in many cases, avoiding consumer tools altogether for client‑specific prompts.
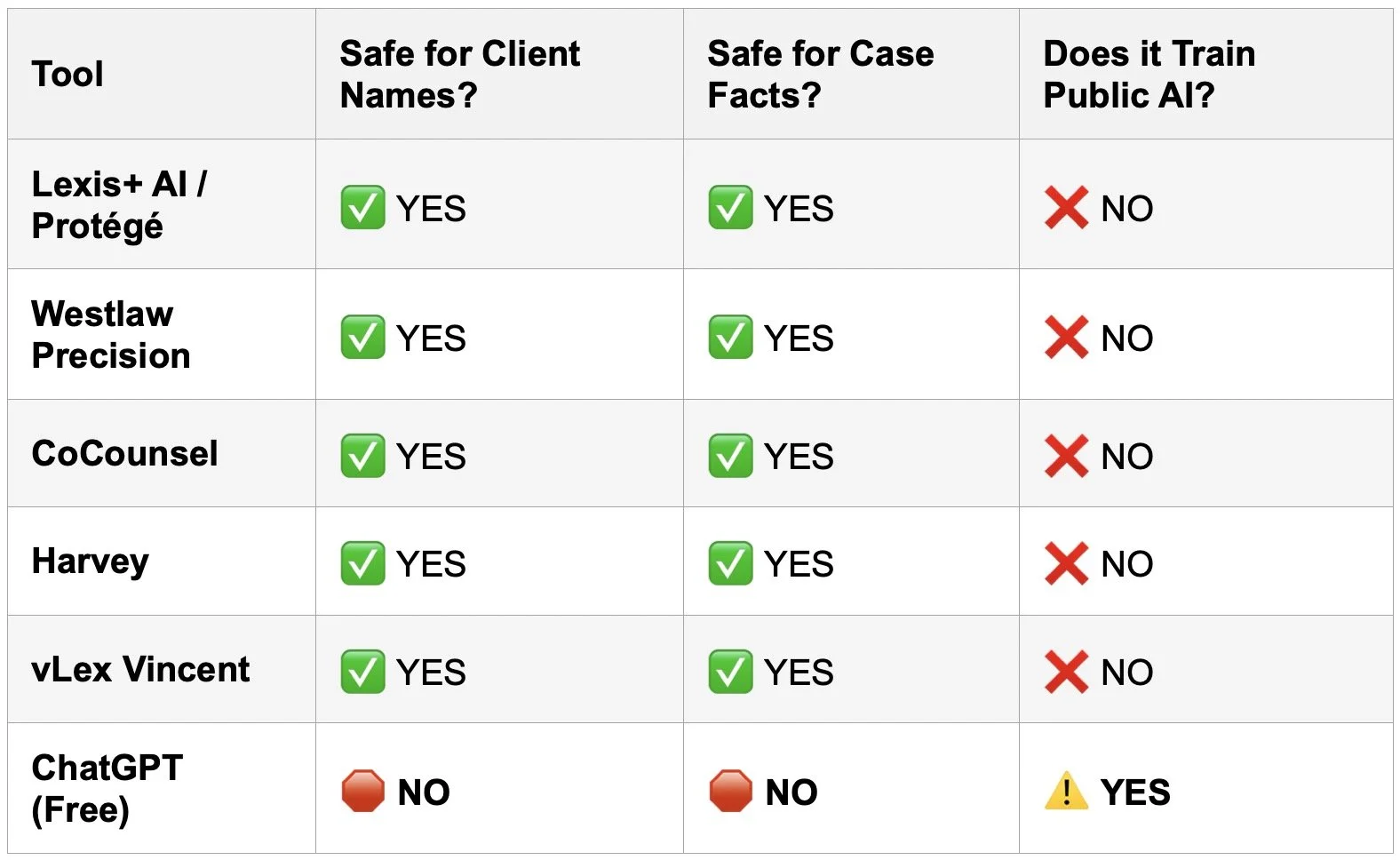
Does a private, paid AI make a difference? Possibly, but only if it is structured like other trusted legal technology. Enterprise or legal‑industry tools that contractually commit not to train on user data and to maintain strict confidentiality can better support privilege claims, because confidentiality and reasonable expectations are preserved. Tools like Lexis‑style or Westlaw‑style AI offerings, deployed under robust business associate and security agreements, look more like traditional research platforms or litigation support vendors within Model Rules 5.1 and 5.3, which govern supervisory duties over non‑lawyer assistants. The Tech‑Savvy Lawyer.Page has emphasized this distinction, encouraging lawyers to favor vetted, enterprise‑grade solutions over consumer chatbots when client information is involved.
Enterprise AI Vetting Checklist for Lawyers: Contracts, NDA, No Training
The tech‑savvy lawyer in 2026 is not the one who uses the most AI; it is the one who knows when not to use it. Before entering client facts into any generative AI, lawyers should ask: Is this tool configured to protect client confidentiality? Have I satisfied my duties of competence and communication by explaining the risks to my client (Model Rules 1.1 and 1.4)? And if a court reads this platform’s privacy policy the way Judge Rakoff did, will I be able to defend my privilege claims with a straight face to a court or to a disciplinary bar?
AI may be a powerful drafting partner, but it is not your co‑counsel and not your client’s confidant. The tech‑savvy lawyer—of the sort championed by The Tech‑Savvy Lawyer.Page—treats it as a tool: carefully vetted, contractually constrained, and ethically supervised, or not used at all. 🔒🤖