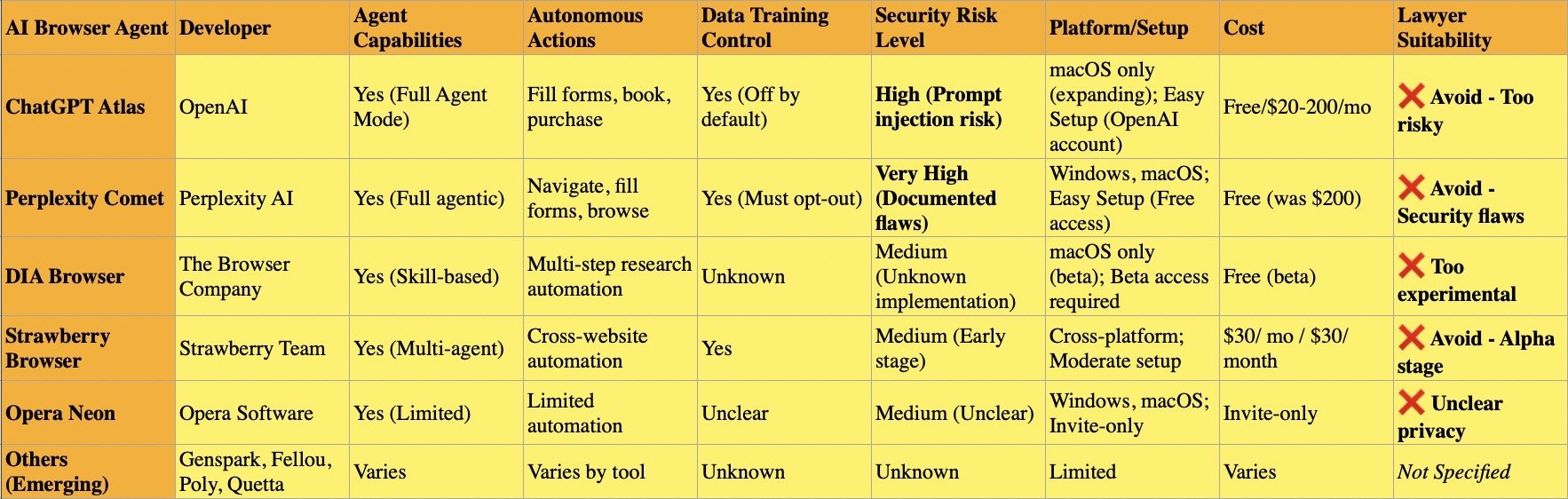
Microsoft 365 Copilot integrates AI across Word, Outlook, and Teams—applications lawyers use hundreds of times daily. The AI drafts documents, summarizes emails, and analyzes meeting transcripts. Most firms that subscribe to Microsoft 365 have Copilot enabled by default in recent licensing agreements, yet many attorneys remain unaware their correspondence flows through generative AI systems.
Adobe Acrobat now automatically recognizes contracts and generates summaries with AI Assistant. When you open a PDF contract, Adobe's AI immediately analyzes it, extracts key dates and terms, and offers to answer questions about the document. This processing occurs before you explicitly request AI assistance.
Legal research platforms embed AI throughout their interfaces. Westlaw Precision AI and Lexis+ AI process search queries through generative models that hallucinate incorrect case citations 17% to 33% of the time according to Stanford research. These aren't separate features—they're integrated into the standard search experience lawyers rely upon daily.
Practice management systems deploy hidden AI for intake forms, automated time entry descriptions, and matter summaries. Smokeball's AutoTime AI generates detailed billing descriptions automatically. Clio integrates AI into client relationship management. These features activate without explicit lawyer oversight for each instance of use.
Communication platforms present particularly acute risks. Zoom AI Companion and Microsoft Teams AI automatically transcribe meetings and generate summaries. Otter.ai's meeting assistant infamously continued recording after participants thought a meeting ended, capturing investors' candid discussion of their firm's failures. For lawyers, such scenarios could expose privileged attorney-client communications or work product.
The Compliance Framework
Establishing ethical AI use requires systematic assessment. First, conduct a comprehensive technology audit. Inventory every software application your firm uses and identify embedded AI features. This includes obvious tools like research platforms and less apparent sources like PDF readers, email clients, and document management systems.
Second, evaluate each AI feature against confidentiality requirements. Review vendor agreements to determine whether the AI provider uses your data for model training, stores information after processing, or could disclose data in response to third-party requests. Grammarly, for example, offers HIPAA compliance but only for enterprise customers with 100+ seats who execute Business Associate Agreements. Similar limitations exist across legal software.
Third, implement technical safeguards. Disable AI features that lack adequate security controls. Configure settings to prevent automatic data sharing. Adobe and Microsoft both offer options to prevent AI from training on customer data, but these protections require active configuration.
Fourth, establish firm policies governing AI use. Designate responsibility for monitoring AI features in licensed software. Create protocols for evaluating new tools before deployment. Develop training programs ensuring all attorneys understand their obligations when using AI-enabled applications.
Fifth, secure client consent. Update engagement letters to disclose AI use in service delivery. Explain the specific risks associated with processing confidential information through AI systems. Document informed consent for each representation.
The Verification Imperative
ABA Formal Opinion 512 emphasizes that lawyers cannot delegate professional judgment to AI. Every output requires independent verification. When Westlaw Precision AI suggests research authorities, lawyers must confirm those cases exist and accurately reflect the law. When CoCounsel Drafting generates contract language in Microsoft Word, attorneys must review for accuracy, completeness, and appropriateness to the specific client matter.
The infamous Mata v. Avianca case, where lawyers submitted AI-generated briefs citing fabricated cases, illustrates the catastrophic consequences of failing to verify AI output. Every jurisdiction that has addressed AI ethics emphasizes this verification duty.
Cost and Billing Considerations
Formal Opinion 512 addresses whether lawyers can charge the same fees when AI accelerates their work. The opinion suggests lawyers cannot bill for time saved through AI efficiency under traditional hourly billing models. However, value-based and flat-fee arrangements may allow lawyers to capture efficiency gains, provided clients understand AI's role during initial fee negotiations.
Lawyers cannot bill clients for time spent learning AI tools—maintaining technological competence represents a professional obligation, not billable work. As AI becomes standard in legal practice, using these tools may become necessary to meet competence requirements, similar to how electronic research and e-discovery tools became baseline expectations.
Practical Steps for Compliance
Start by examining your Microsoft Office subscription. Determine whether Copilot is enabled and what data sharing settings apply. Review Adobe Acrobat's AI Assistant settings and disable automatic contract analysis if your confidentiality review hasn't been completed.
Contact your Westlaw and Lexis representatives to understand exactly how AI features operate in your research platform. Ask specific questions: Does the AI train on your search queries? How are hallucinations detected and corrected? What happens to documents you upload for AI analysis?
Audit your practice management system. If you use Clio, Smokeball, or similar platforms, identify every AI feature and evaluate its compliance with confidentiality obligations. Automatic time tracking that generates descriptions based on document content may reveal privileged information if billing statements aren't properly redacted.
Review video conferencing policies. Establish protocols requiring explicit disclosure when AI transcription activates during client meetings. Obtain informed consent before recording privileged discussions. Consider disabling AI assistants entirely for confidential matters.
Implement regular training programs. Technology competence isn't achieved once—it requires ongoing education as AI features evolve. Schedule quarterly reviews of new AI capabilities deployed in your software stack.
Final Thoughts 👉 The Path Forward